Toggletip
Toggletips use the disclosure pattern to toggle the visibility of a popover. They display additional, hidden information upon the click of a UI trigger element and can contain interactive elements.
Overview
Toggletips reveal supplemental content when a user clicks a button or another UI element and remains actively open until a user dismisses it. A toggletip is comprised of a UI trigger and the popover component. Use the disclosure pattern to design supplemental content within the component. Toggletips can include a wide variety of information and interactive elements as long as accessibility requirements are maintained including focus order and ensuring all functionality is operable through a keyboard interface.
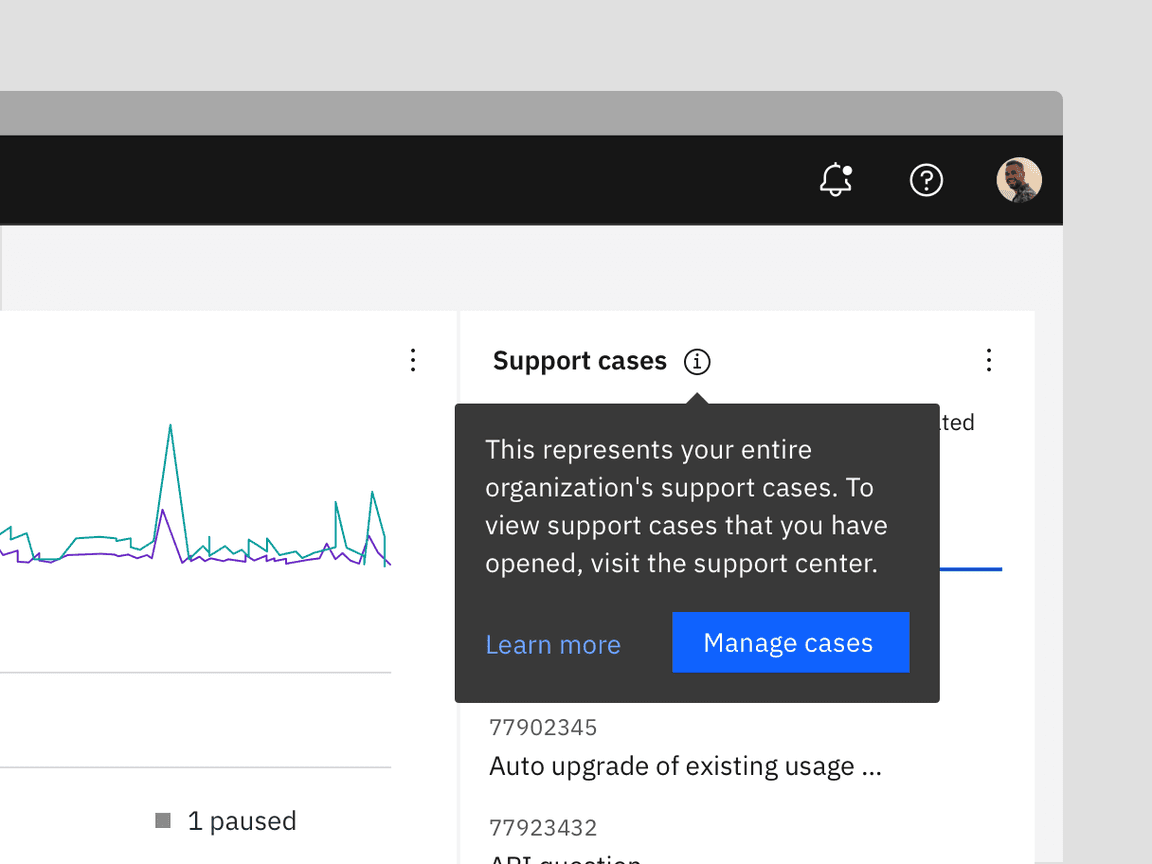
Toggletips verses Tooltips
Toggletips and tooltips are similar visually and both contain a popover and
interactive trigger element. The two components differ in the way they are
invoked and dismissed and if the user must interact with the contents. A tooltip
is exposed on Hover or Focus when you need to expose brief, supplemental
information that is not interactive. A toggletip is used on Click and Enter
when you need to expose interactive elements, such as button, that a user needs
to interact with.
The exception here is that definition tooltip can be invoked on either Hover
or Click depending on use case.
When to use
- Use when an interactive element must be placed within the popover
- Use for quick, in context editing
- Use for filter panels that overlay content
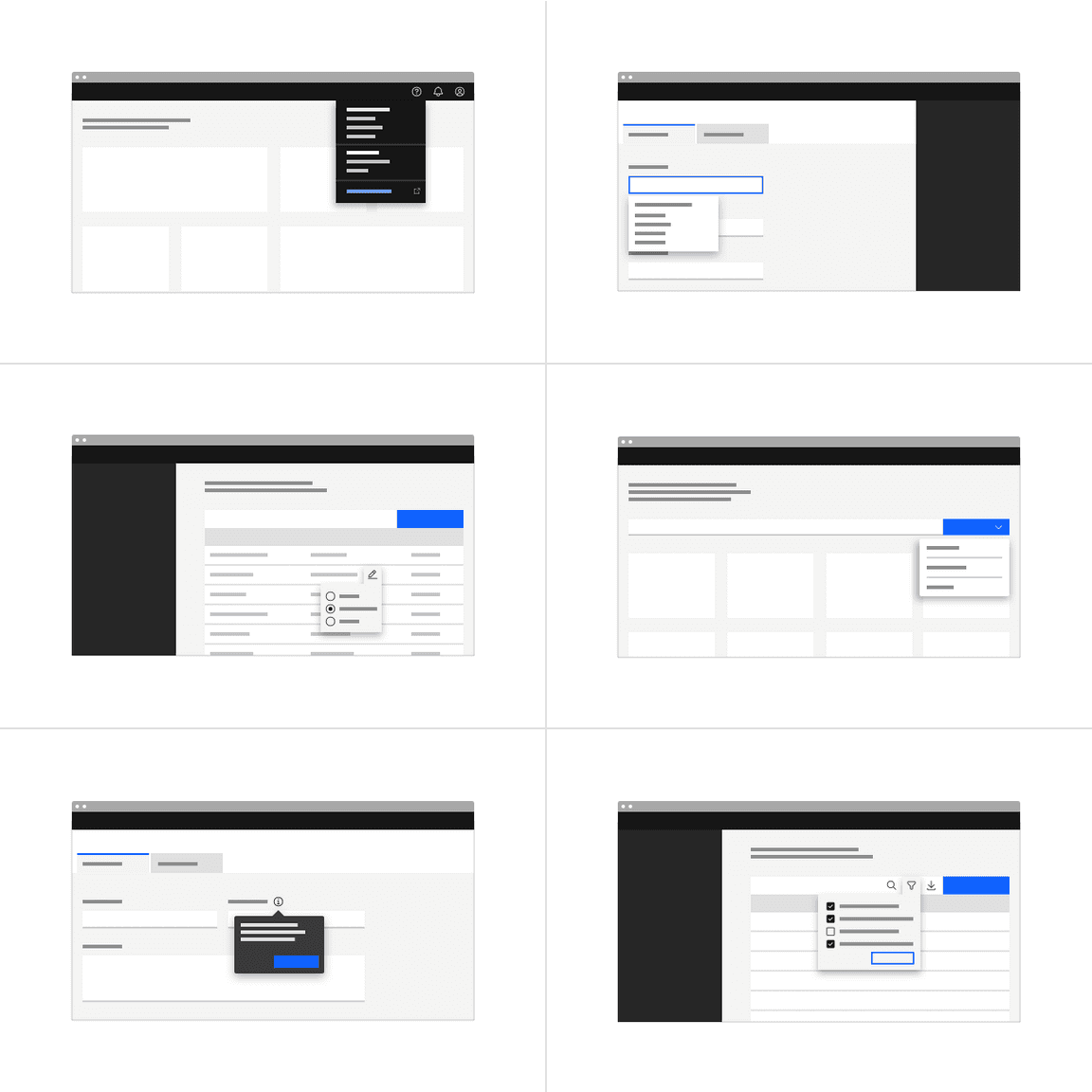
The examples above are patterns. Carbon currently only supports the basic toggletip outlined below. In the future, other toggletip styles will be available.
When to not use
Don’t use to present critical information or request required input needed to complete a workflow. Use the modal component instead.
Live demo
<Toggletip><ToggletipButton label="Additional information"><Information /></ToggletipButton><ToggletipContent><p>Custom content here</p></ToggletipContent></Toggletip>
Anatomy
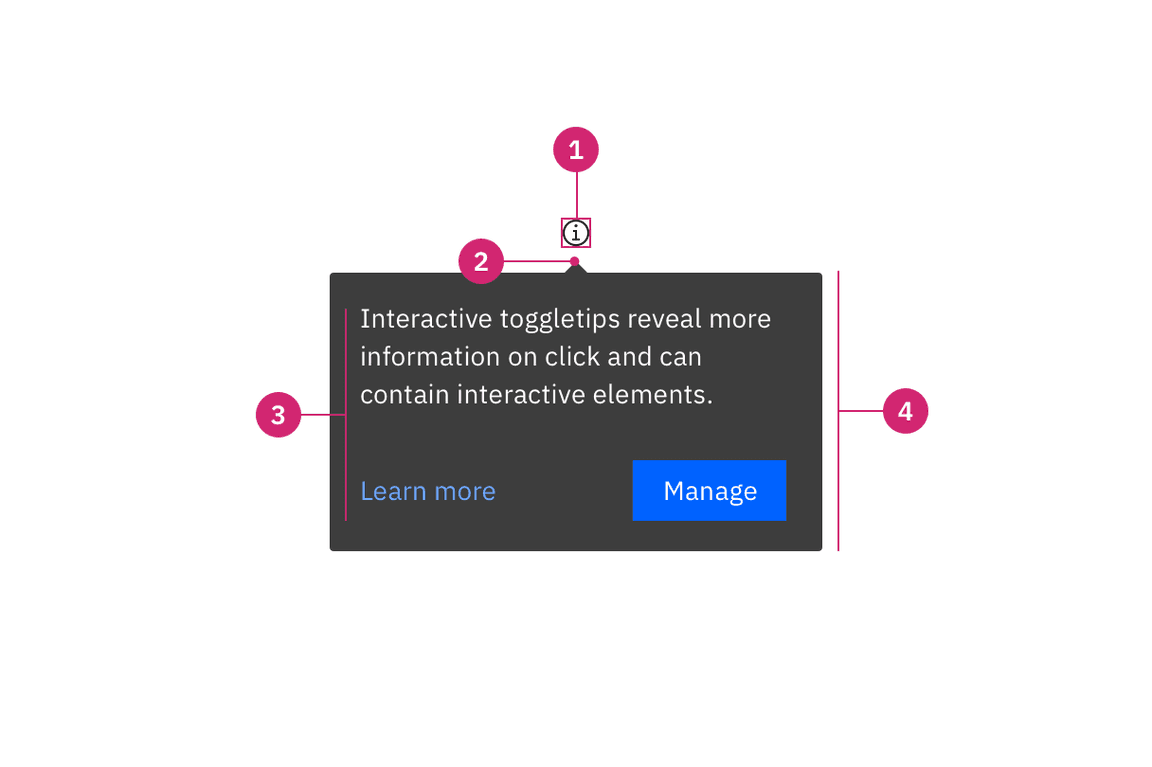
- UI trigger button: Usually a button but as long as the trigger is interactive, it can visually change its shape and size depending on the use case.
- Tip: An indicator that is added to a popover container to help show the relationship between the popover and where it was triggered from. Toggletips can utilize no tip, caret tip, or tab tip types.
- Content area: Varies based on use case and follows disclosure guidelines.
- Popover container: Area that contains text and interactive elements.
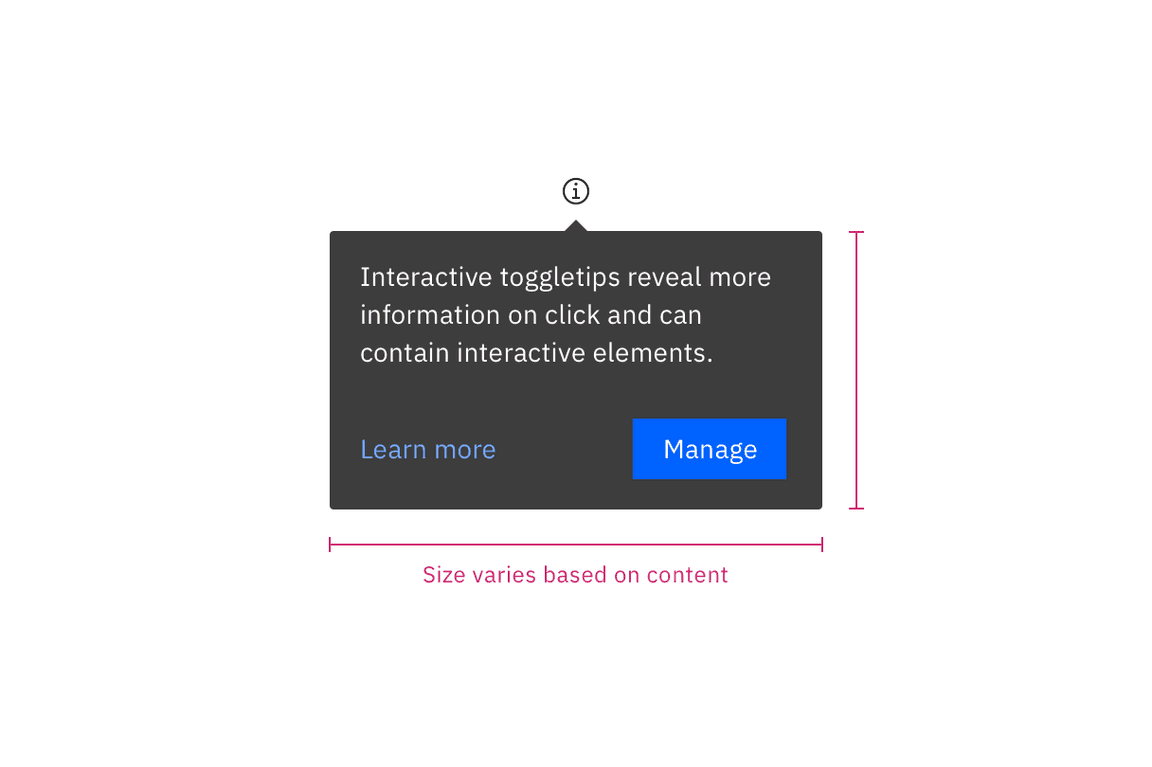
Sizing
The width and height of a popover container can vary depending on the amount of content placed within it. We recommend to not exceed a popover width size of four columns. Refer to the popover component for more specifications.
Placement
Toggletips can be used on various part of the UI including, but not limited to, headers, data tables, side panels, modals, and read only cards. When active, the toggletip popover may be positioned top, bottom, left, or right to the UI trigger.
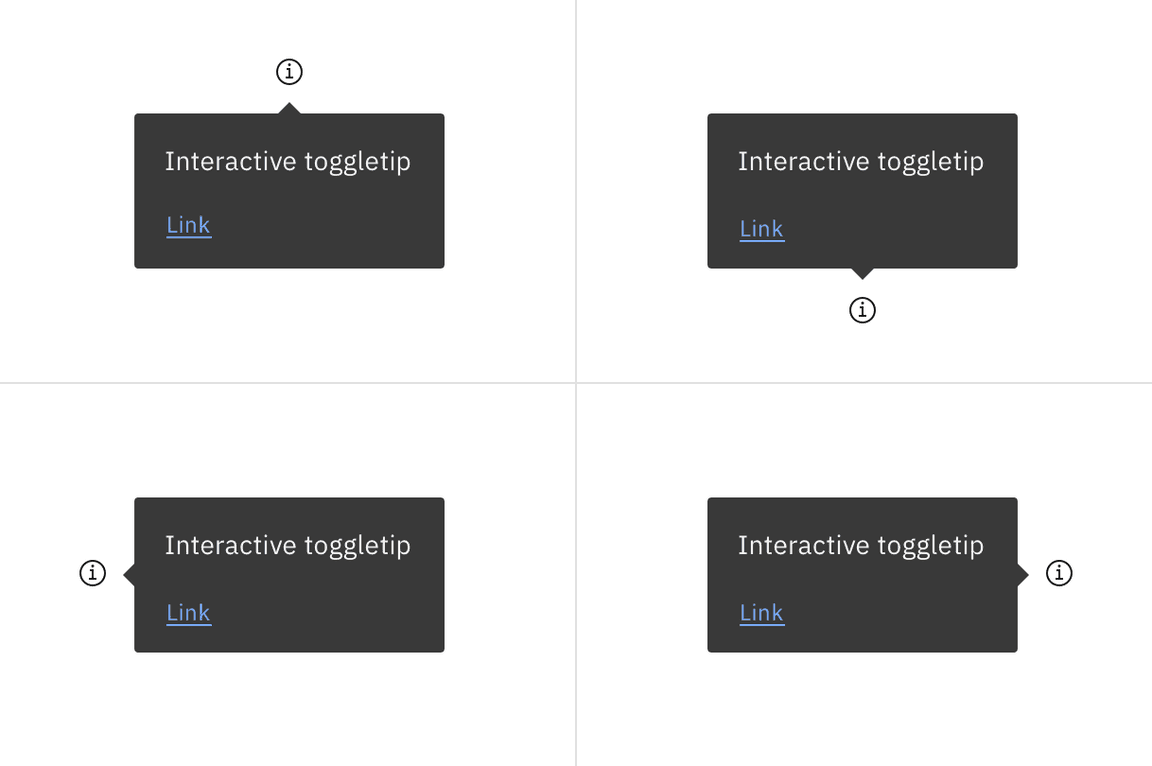
Placement of a popover in relation to the trigger depends on the type of popover used. Visit the popover component for specific guidelines for no tip, caret tip, and tab tip types.
Content
Main elements
Heading, body, and footer content can vary based on your use case. To see examples of content used within toggletips, visit the disclosure pattern.
Interactive tooltips may contain rich text and other interactive elements like buttons or links and must remain actively open until a user dismisses the toggletip. Maintain accessibility requirements including focus order and ensure all functionality is operable through a keyboard interface.
Overflow content
Since the toggletip uses the flexible popover component and disclosure pattern, scrolling is usually not needed. If scrolling is needed, in a dropdown like situation for instance, then the body section should scroll vertically with the header and footer remaining fixed in place if those elements are present. Do not scroll horizontally or let content bleed off the page.
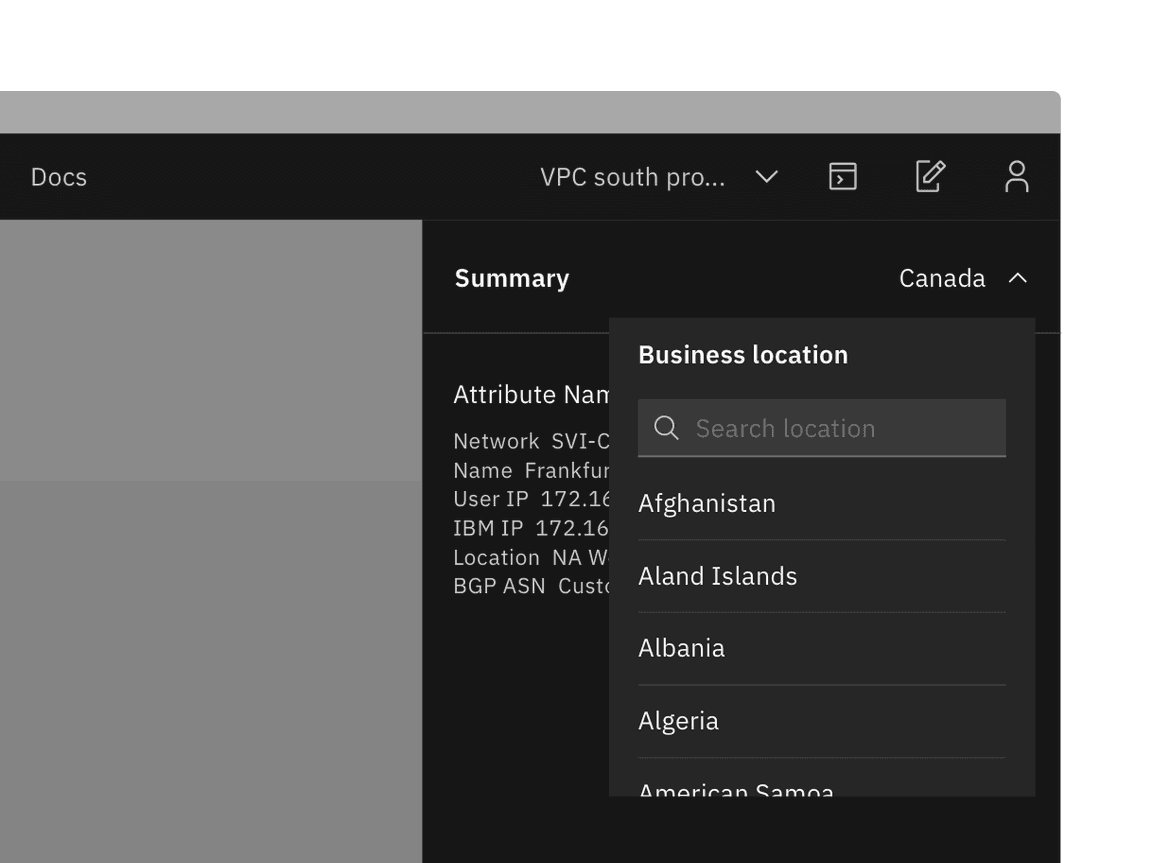
Example of when to scroll within a toggletip. This example is a pattern and is currently not offered as a component.
Further guidance
For further content guidance, see Carbon’s content guidelines).
Behaviors
States
The toggletip component has two states—active and inactive. By default, the
toggletip is hidden and inactive. Toggletips are displayed on Click and
Enter.
Interactions
Mouse
Toggletips are triggered on Click and is dismissed by clicking anywhere
outside the toggletip’s active popover or UI trigger.
Keyboard
Users can trigger a toggletip by pressing Enter or Space while the trigger
element has focus. Users can dismiss a toggletip by pressing Escape. For
additional keyboard interactions, see the accessibility tab.
Screen readers
VoiceOver: Users can trigger a toggletip by pressing Enter or Space while
the trigger element has focus.
JAWS: Users can trigger a toggletip by pressing Enter or Space while the
trigger element has focus.
NVDA: Users can trigger a toggletip by pressing Enter or Space while the
trigger element has focus.
Related
Popover
Popovers are used as a base layer in some of our components like tooltips, overflow menus, and dropdown menus. For further guidance, see Carbon’s popover component.
Disclosure
Disclosures use popovers as a base layer. Disclosures are comprised of a popover container, text, and interactive elements. Interactive elements are kept in the tab order of the page. Further guidance on the disclosure pattern coming soon.
Tooltip
Tooltips display additional information upon hover or focus. The information included should be contextual, helpful, and nonessential while providing that extra ability to communicate and give clarity to a user.
Feedback
Help us improve this component by providing feedback, asking questions, and leaving any other comments on GitHub.